Table of Contents
Definition WINS
WINS is a name resolution service for Windows networks that maps hostnames on a network to their network IP addresses. Its abbreviation is the abbreviation for Windows Internet Naming Service. It converts NetBIOS names to IP addresses on a LAN or WAN.
How does WINS work?
WINS (Windows Internet Naming Service) Name resolution software from Microsoft that ran in Windows servers at the time networks gets converted to IP. Windows workgroup PCs use NetBIOS names, and before Windows XP, required this service to convert the names to IP addresses.
Windows PCs identified themselves to it so other Windows PCs could find their IP addresses. It allowed machines in one LAN segment to locate machines in another by name. Hence the word “internet” in WINS referred to multiple company networks, not the global Internet.
When DHCP assigned a computer an IP address, Its database was updated. In a Windows-only network, It is useful to query for name resolution. In a mixed environment, the Unix machine questions the DNS server, which, starting in Windows 2000, was customized by It. See DNS and DHCP.
Uses
This resolution service is useful on any network with clients that use NetBIOS names. It also applies primarily to older applications and machines running older versions of Windows, those that get released before Windows 2000, Windows XP, and Windows Server 2003.
Like DNS, WINS uses a distributed client/server system to keep mapping computer names to addresses. We can configure Windows clients to use primary and secondary it servers that dynamically update name/address pairings as computers join and leave the network. The dynamic behavior of it means that it also supports networks that use DHCP.
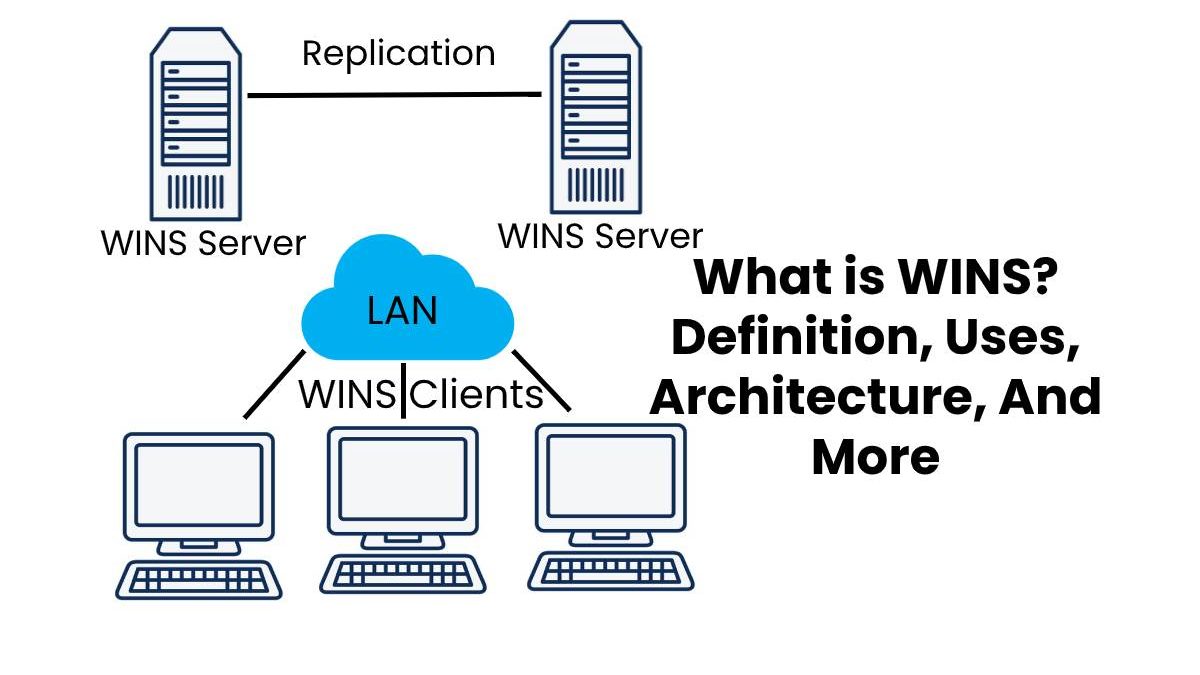
Architecture
The WINS system consists of two main components:
The WINS server manages the NetBIOS name map.
It clients, which use NetBIOS names for their resources that are plan to its server to map to IP addresses, and which query the WINS server for addresses to other NetBIOS resources on the network.
In addition to these components, there is also its database, which is the name “map,” the dynamically upgrade list of NetBIOS names and identifies IP addresses.
In exceptional cases, there may be a WINS proxy, which is another type of client that can act on behalf of computers that are not WINS-enabled. It will allow users to potentially use it with devices that would not otherwise have access to the program.