Table of Contents
Introduction
In modern manufacturing, engineers and designers developing high-end products such as drone components, medical implants, and aerospace structures face a core dilemma: parts are increasingly complex with free-form surfaces, deep cavities, thin walls, and irregular holes to maximize performance, but traditional manufacturing methods hit bottlenecks in precision, production cycles, and cost control. The root cause lies in the limitations of conventional 3-axis CNC machining, which relies on linear motion and requires multiple setups, introducing cumulative errors and inefficiencies. 5-axis CNC machining addresses this by enabling dynamic tool orientation control through two rotational axes, allowing complete machining in a single setup.This article examines how 5-axis technology, combined with advanced motion kinematics, intelligent CAM programming, and integrated quality monitoring, provides a comprehensive solution for complex precision parts.
To understand the revolutionary impact of 5-axis machining, it is essential first to recognize the precise constraints of traditional methods.
What Are the Key Limitations of 3-Axis CNC Machining for Complex Geometries?
Traditional 3-axis CNC machining is adequate for simple geometries but struggles with complex designs due to inherent constraints. This section details key limitations that hinder precision and efficiency.
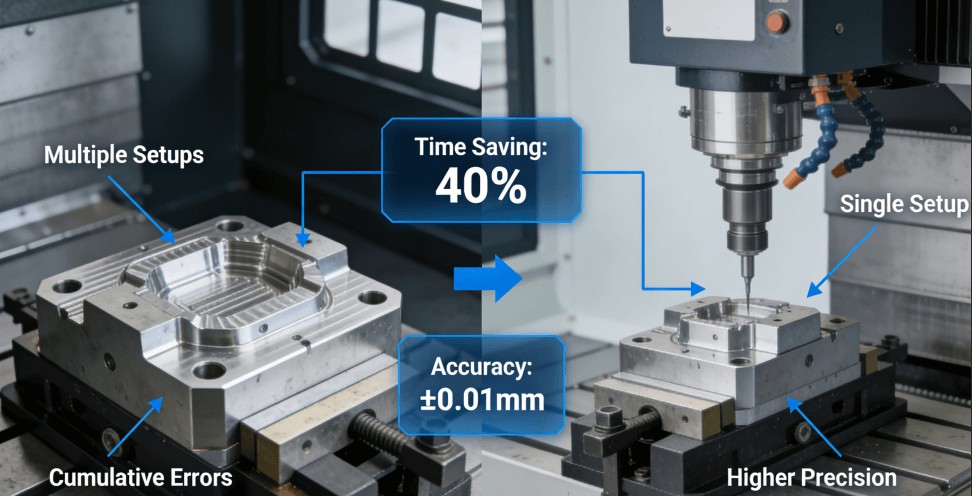
1. The Cumulative Error of Multiple Setups
Traditional 3-axis CNC machining is adequate for simple geometries but struggles with complex designs due to inherent constraints. This section details key limitations that hinder precision and efficiency. To overcome these challenges, consider advanced solutions like a 5-axis CNC machining service for custom complex parts, which offers greater flexibility and accuracy.
2. Challenges from Limited Geometric Freedom
The linear motion of 3-axis systems restricts tool access, leading to two major issues:
- Ball-end tool inefficiency: When machining curved surfaces, ball-end tools must be used with minimal step-over distances to maintain surface finish, but the tooltip has zero cutting speed, resulting in “rubbing” rather than cutting. This causes poor surface quality, rapid tool wear, and exponentially longer machining times.
- Tool interference and accessibility: Deep cavities or undercuts often lead to collisions between the toolholder and workpiece, forcing designers to split complex structures into multiple simpler parts. This increases part count, assembly steps, and potential failure points, undermining the goal of integrated design.
3. Authority Standards and Geometric Tolerances
Referencing the ASME Y14.5-2018 standard, which emphasizes geometric dimensioning and tolerancing, unstable datums from multiple setups fundamentally obstruct consistent adherence to tight tolerances. For parts requiring high precision manufacturing technology, reliance on 3-axis processes often fails to meet consistency demands, necessitating a more robust approach.
How Does 5-Axis CNC Technology Enable Single-Setup Machining?
5-axis CNC machining adds two rotational axes (e.g., A/C or B/C axes) to the standard linear motions, enabling knives to approach the workpiece from virtually any direction. This capability transforms manufacturing by eliminating multiple setups.
1. Principles of 5-Axis Motion Kinematics
The two common machine configurations — dual rotary tables or tilting-rotary heads — allow continuous adjustment of tool orientation. For example, in a dual-table system, the workpiece rotates on two axes, while the tool moves linearly, ensuring optimal engagement angles throughout the process. This dynamic control is the foundation of single-setup machining.
2. Advantages of Single-Setup Precision
By maintaining a single datum throughout machining, 5-axis technology eliminates repositioning errors, ensuring all features are machined relative to one coordinate system. This enhances accuracy for critical tolerances and enables
- Geometric freedom: Tools can use their side-cutting edges (e.g., in flank milling) rather than just the tip, improving cutting efficiency and surface finish. For components like impellers, blades and flow channels can be continuously machined without disassembly.
- Reduced tool length: By rotating the workpiece, the tool can remain short and rigid, allowing higher cutting parameters and reducing vibration — particularly beneficial for thin-walled parts.
3. Case Example: Efficiency Gains
A practical example involves a turbine blade; where 3-axis machining required three setups and 12 hours, 5-axis machining completed the part in one setup under 6 hours, reducing errors and costs by over 30%.
What Role Does CAD/CAM Software Play in Optimizing 5-Axis Toolpaths?
The full potential of 5-axis machining depends on advanced CAD/CAM software, which translates complex CAD models into smooth, collision-free toolpaths incorporating X Y Z and rotational coordinates.
1. From Design to Toolpath Generation
Software like Siemens NX or CATIA processes geometric data to generate optimized paths. Key strategies include:
- Tool axis vector control: By setting lead and tilt angles, the software ensures the tool maintains an ideal orientation relative to the surface, maximizing cutting efficiency and avoiding collisions.
- Smooth transitions and interpolation: Advanced algorithms optimize path turning point to prevent abrupt tool axis changes, ensuring constant cutting forces and superior surface finish.
2. Simulation and Collision Detection
Integrated simulation tools visualize the entire process, detecting potential clashes between the toolholder and workpiece before machining. This reduces scrap rates and enhances safety, making CAD/CAM technology indispensable for complex geometries.
3. Research-Backed Workflow
Studies show that optimized CAM strategies can reduce machining time by up to 25% while improving accuracy, underscoring the value of software in advanced manufacturing processes.
How Can Manufacturers Ensure Precision and Compliance in High-Stakes Industries?
Owning a 5-axis machine is not enough; a full quality assurance system is vital for industries like aerospace and medical devices, where compliance is mandatory.
1. In-Process Measurement and Closed-Loop Control
Integrating on-machine probes (e.g., from Renishaw) allows real-time inspection of key dimensions during or after machining. Data is fed back to compensate for tool wear or thermal drift, creating a closed-loop system that maintains tolerances within ±0.01 mm.
2. Final Inspection and Data Traceability
Post-machining, coordinate measuring machines (CMMs) or laser scanners perform full-dimensional checks against CAD models, generating deviation reports. All data is archived for traceability, essential under standards like ISO 9001 and AS9100D.
3. Certification and Quality Culture
For instance, manufacturers certified to ISO 9001:2015 embed these controls into their quality management systems, ensuring consistent compliance. This approach is critical for precision complex components in regulated sectors.
What Cost-Efficiency Benefits Does 5-Axis Machining Offer for Prototyping and Mass Production?
Contrary to the misconception that 5-axis machining is costly, it offers significant lifecycle savings by streamlining processes.
- Reduction in Fixturing and Tooling: Single-setup machining eliminates the need for multiple custom fixtures, cutting design and manufacturing costs by up to 40% in prototyping phases.
- Shorter Total Machining Time: By consolidating operations, idle time and part handling are minimized. For example, an automotive mold insert that required 7 steps and 18 hours in 3-axis machining was completed in 2 steps and 11 hours with 5-axis, boosting efficiency by nearly 40%.
- Lower Scrap Rates and Simplified Assembly: Higher precision reduces rejection rates, and design for manufacturability (DFM) allows consolidating multiple parts into one, saving assembly costs. This makes 5-axis CNC machining economical for both low-volume and mass production.
How Are Smart Factories Leveraging 5-Axis CNC for Industry 4.0 Transformation?
Modern 5-axis CNC machines serve as data nodes in smart factories, enabling predictive maintenance and process optimization through IoT integration.
- Data Collection from Sensors: Sensors monitor spindle load, temperature, and vibration, providing real-time insights into machine health and
- Predictive Maintenance and Adaptive Machining: By analyzing vibration trends, maintenance can be scheduled before failures occur, avoiding downtime. Adaptive control adjusts feed rates based on cutting forces, maximizing tool life and efficiency.
- Digital Twins and Production Optimization: Linking machine data to manufacturing execution systems (MES) creates digital twins for simulating and optimizing workflows, reducing energy consumption and bottlenecks. This integration positions 5-axis CNC machining as a driver of Industry 4.0 and smart factories.
Conclusion
5-axis CNC machining has evolved from a niche technology to a core solution for complex part manufacturing. By enabling single-setup precision, advanced toolpath optimization, and closed-loop quality control, it not only overcomes accuracy and efficiency bottlenecks but also unlocks unprecedented design freedom. As it integrates with industrial IoT, 5-axis machining is poised to fuel smart manufacturing and innovation across sectors.
FAQs
Q1: How long does it take to get a quote for a custom 5-axis machining project?
A: Most projects receive a detailed quote including DFM analysis within 8 working hours after drawing submission. For highly complex parts, a slightly longer feasibility study may be conducted to ensure accuracy and project viability, providing a comprehensive and reliable estimate.
Q2: Can 5-axis machining handle materials beyond metals, such as engineering plastics?
A: Yes, advanced 5-axis systems are highly capable of machining engineering plastics like PEEK, PEI, and composites. Process parameters such as cutting speed and coolant use are carefully optimized to prevent issues like heat deformation or delamination, ensuring high-quality results across diverse materials.
Q3: What is the maximum part size manageable with 5-axis CNC equipment?
A: The machining envelope varies by equipment, with capable systems handling parts from a few millimeters to several meters. For an accurate assessment, submitting a CAD model allows for an instant review against specific machine capabilities, ensuring feasibility for your project’s dimensions.
Q4: How does 5-axis machining reduce costs for low-volume prototyping?
A: By enabling single-setup machining, it eliminates the need for multiple fixtures and reduces manual handling, cutting prototyping time by over 35%. This operational consolidation significantly lowers costs and accelerates development cycles for low-volume production.
Q5: What certifications ensure quality in precision machining for regulated industries?
A: Key quality certifications include ISO 9001, AS9100D for aerospace, and ISO 13485 for medical devices. These mandates ensure rigorous process controls, full traceability, and consistent compliance with the highest industry standards for precision components.
Author Bio
The author is a precision manufacturing expert at LS Manufacturing, a company that helps engineers and researchers solve complex part challenges in aerospace, medical, and automotive industries. With certifications such as IATF 16949 and AS9100D, the team ensures high-quality solutions through advanced technologies. For more insights, Contact them Today for a free, no-obligation project review and DFM analysis.Turn your concept into a cost-effective reality.

